XML files for an increased visibility

Publishing your latest research results is not an easy task. First, you need to create a coherent document, that conveys the message in a clear and understandable way. Secondly, you need to go through different editing stages to create that desired, polished style. To help you to understand what stages lie ahead of you, just click on the links below:
- language editing
- copyediting
- typesetting (known also as technical editing)
- proofreading
- XML publication (academic publishing only).
The whole process of manuscript production can be really time-consuming and overwhelming. Once finished, you most probably are just wishing to have your work published. Yet have you ever considered what the different publication ways are and what results they can obtain?
From traditional to modern publishing
In the past, all the content accepted for publication was printed out and distributed. Academic works were usually acquired by institutional libraries, as the print was usually too expensive for an individual user.
However, everything changed with the appearance of the Internet. Online publishing revolutionized the way publishers work, as content sharing became faster, cheaper and virtually limitless. Individuals can now access subject matter in an instant way, from anywhere on the globe.
To read more about the differences between print and online publishing, check this article.
Academic publishing today
Nowadays, an article or book must have its online counterpart available to achieve real visibility and popularity. To do that, documents are converted into electronic formats and hosted in repositories, virtual libraries and on publishing platforms. This is especially true in science, where access to the latest research results is of the utmost importance.
Professional publishing platforms strive to develop the best technology and solutions to enhance the online reading experience. Amongst the most popular features that readers can enjoy are options such as instant content sharing, alerting service, saving the documents for a later read and downloading citation formats.
Online publication formats
Amongst the various formats used for online publications, PDF has gained so far the widest popularity. PDFs can be opened and read directly on a screen, both on a computer and on a mobile device, and also downloaded from the web for later use. Books in addition to PDFs, are released in special files readable on portable devices, such as MOBI and EPUB.
These new publication ways aim to increase the visibility and the readership of published works. However having content available online can turn out to be insufficient, as the sheer number of published documents makes promotion difficult. Publishers have started to look for methods enabling discoverability, utilizing the latest technological achievements. This is when exploring the possibilities of an XML format started.
What is an XML file?
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a language that enables publishers to store and transport information in a structured manner. XML files differ from HTML in the sense that they are used to describe data, while HTMLs are used to display data.
The other important difference between XML and HTML lies in the tags. In HTML these are predefined, while in XML the user defines their own set of tags making XMLs extremely versatile:
- XML documents are plain text files, while HTML documents are coded with a particular set of tags that indicate how content should be displayed in a browser
- XML does not display the data. Instead, it stores information that can be used for many other purposes
- XML is often used to store and organize large amounts of information, as in databases and web services.
- XML can also act as an intermediary between different systems, allowing them to exchange information in a common format.
In short, XML is a markup language that provides structure and meaning to data, while HTML is a presentation language that displays content on web pages.
XML can be used for many different purposes:
- storing and transporting data
- creating templates for webpages
- exchanging data between applications.
Its flexibility makes it an invaluable tool for developers, enabling them to efficiently interact with databases and other systems.
XML files are also much smaller than files created using traditional methods, making them ideal for use on websites or mobile applications where speed is important.
XML files in academic publishing
When the XML format entered the scientific world, content sharing and content discoverability became easier than ever before. One of the most important features of XML academic files is their ability to exchange data across multiple platforms.
Abstracting and indexing services that catalogue academic content usually expect to have the documents delivered directly to their portals. XML files allow for just that. When publishers create them for their publications, the technology automatically exports them to all third-party services where the content is to be made visible.
What is more, an XML enables better control of information flow, making sure that the shared data meets the expected standards. All the most important indexing services, such as Clarivate, Scopus, EBSCO or ProQuest, rely on the XML metadata delivered by publishers.

Corrections and document management
XML files offer also a cost-effective, streamlined approach to managing documents. Whenever an error in the data appears, XML files can be easily updated or modified. Every change to existing data triggers automatic export to third-party services to ensure its correctly reflection on their side. This feature enables easier collaboration between authors, editors, publishers and indexing services across the entire publishing cycle.
JATS XML files
XML files are available in different formats; of which one has become especially significant in academic publishing: JATS format (Journal Article Tag Suite). This is an open, XML-based standard for publishing and archiving journal articles. It is widely used by major publishers, including the De Gruyter Publishing Group, of which Sciendo is a part. As a result of its widespread adoption, JATS has become the de facto standard for scholarly publications.
JATS XML files provide a consistent way to store bibliographic data about an article:
- they include the author’s information
- title, abstract and list of keywords
- subject categories
- digital object identifiers (DOIs)
- copyright statements.
JATS XML metadata is typically requested by abstracting and indexing services that store academic content. Professional publishing platforms export the data in an automatic manner, making them available in these services for scientists from all over the world.
JATS XML files are an invaluable tool for modern scientific publishing. They not only facilitate the storage of bibliographic data but also enable researchers to access relevant information quickly and easily from anywhere in the world.
Book and article XML metadata
In academic publishing, data in an XML format is created for all articles and book chapters. There are two ways to make this happen – create XML files for all the available text, including graphics and tables, or for academic metadata only. XML metadata is usually sufficient when it comes to cooperation with indexing services, as most of them are of the abstracting type and do not include full-text versions.
XML metadata includes:
- the document title
- article type (if applicable, for example: review, technical paper, editorial, etc.)
- abstract
- DOI number
- list of keywords
- list of authors with their affiliations
- cover date and publication date
- bibliography
- copyright information.
Full-text XML publication
In addition to metadata, many academic publishers prepare also full versions of papers in an XML format. Such a process is more time-consuming and more expensive, but having the whole paper converted into the XML format provides additional benefits:
- documents can be read directly on the screen, without the need to download the PDF
- XML text adjusts itself to the screens of mobile devices (whereas PDFs must be scrolled), thereby enhancing the reading experience
- papers are searchable for via search engines (whereas PDFs are not), helping to increase the visibility of publications on the Internet.
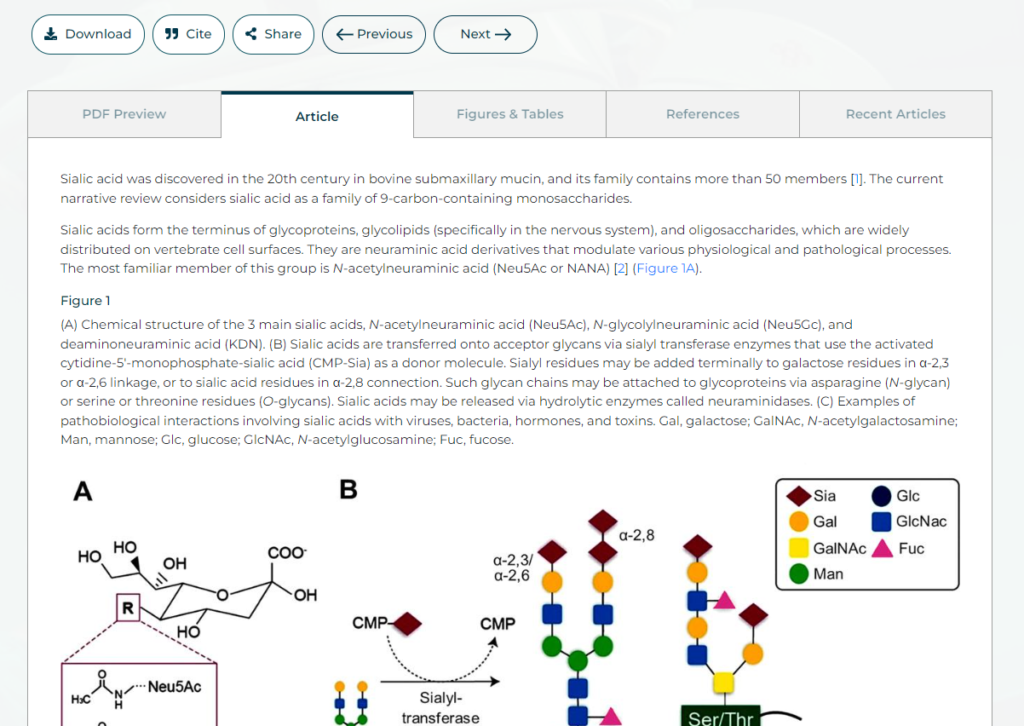
Full-text XML files are becoming increasingly popular with the demand for documents available in this model constantly increasing. XML files allow publishers to store additional structural elements such as figures or tables associated with each paper. This makes them easy to find when searching through large databases or archives with thousands of articles stored in this format.
One of the biggest advantages of this language is the easiness to read the content on a mobile device. This is especially helpful when travelling. With a few clicks, a full version of an article or book chapter becomes available for reading directly on the phone or tablet.
The statistics show that journals that publish in a full-text XML version have increased usage on mobile devices. Moreover, readers more willingly return to them, knowing that their research is easily readable on their portable devices.
Full-text article XML files in indexing services
Full-text article XML files are sometimes required by abstracting and indexing services. PubMed Central, managed by the United States National Library of Medicine, is an example of just a database. Biomedical journals wishing to include their content in this service are required to submit their complete documents in XML format.
On its website, PubMed Central explains its preference with regard to XML files. According to them, XML is the most practical text format, both software- and hardware-independent, and easily adaptable to changes in technology. Existing files can be effortlessly converted to other text types in the future, in the case of different formats becoming predominant. PubMed Central underlines also that XML tagging enables smooth automatic content parsing, facilitating more advanced searching and linking to other related documents.
Benefits of XML publication
XML provides a powerful tool that can be used by developers and publishers to quickly and efficiently create and share content. Publishing in XML provides an array of benefits:
- XML increases the visibility of documents
- makes it easier for readers to find and read papers through search engines
- XML tagging enables for a convenient citing of works in other publications
- documents can be easily shared across different platforms allowing larger audiences to be reached
- helps to ensure that all content is correctly displayed on any device or platform where it is viewed
- XML files are more efficient than traditional methods of document management. They can be used in various ways such as websites or mobile applications.
XML files, especially in JATS format, are an excellent choice for academic publishing because of their versatility, time-saving properties, and their maintenance of quality standards. Having documents available in XML, authors can ensure that their content is properly organized and accessible across multiple platforms with minimal effort on their part.
XML formatting service at Sciendo
Sciendo can convert any academic document into JATS and other XML formats to increase its visibility and to ensure its correct citation. We create XML metadata for all publications on our platform. As an additional service, we prepare also full-text XML files. In the Premier package for journals, we convert all article texts into the XML format.
To find out more about our service, please complete the form.
Publishing your first academic book
If you are an early career scholar who is thinking of writing academic books to advance your career, this article will help you navigate book publishing with more confidence and less stress.
read moreWriting an academic book chapter
In a previous article entitled Publishing your first academic book, we advised early-career researchers to start publishing articles in reputable journals as a way to get experience and build up a career as academic authors. Open-access journals are particularly helpful because they are not behind a paywall and can reach a wider audience.
read moreHow to ensure the originality of your paper and avoid plagiarism
The research process expects ethical behaviour and good practice. As plagiarism and self-plagiarism are on the increase, scientific publishers are using software to detect these instances of scientific misconduct.
read moreBenefits of publishing in an open access journal
Open access publishing is gaining popularity worldwide. Diffusing research findings in an open access journal offers many benefits to academic authors and institutions, which we will discuss in this article.
read morePress release: Learning Analytics: a Metacognitive Tool to Engage Students
The presented study is the result of the research project ‘Open Online Learning for Digital and Networked Society (3.3-LMT-K-712-01-0189)’, funded by the European Social Fund according to the activity ‘Improvement of researchers’ qualification by implementing world-class R&D projects’ of Measure No. 09.3.3-LMT-K-712 under the grant agreement with the Research Council of Lithuania (LMTLT).
read moreFrom Predatory Publishing To Trusted Publishers
The term “predatory publishing” was first used by Jeffrey Beall, an academic who created and maintained a list of potential, possible, or probable predatory journals on his university website.
read more